Table of Contents
Understanding Botox Injections for Migraine Relief
Chronic migraines affect millions of adults, turning daily life into a battle against debilitating pain. For those enduring 15 or more headache days each month, relief often feels out of reach despite traditional treatments. Botox injections for migraines have emerged as a promising option, evolving from its well-known cosmetic applications to a specialized therapy for headache prevention.
Botox, or onabotulinumtoxinA, is a purified neurotoxin that works by blocking the release of chemicals responsible for pain signals in the nervous system. This mechanism helps prevent migraines before they start, particularly for patients with chronic cases unresponsive to other therapies. In 2010, the FDA approved botox for migraines as a preventive treatment, based on clinical evidence showing it reduces headache days by up to 50% in responders, as noted by sources like WebMD and Mayo Clinic. Ideal candidates are adults facing frequent, severe episodes that disrupt work and well-being.
At Charleston Ketamine Center in Mount Pleasant, South Carolina, we integrate Botox therapy for headache prevention with our expertise in ketamine infusions for comprehensive care. Located at 1948 Long Grove Drive #2, our licensed team supervises every neurotoxin treatment for chronic headaches, offering personalized protocols that address both pain and underlying mood challenges. Free consultations ensure a safe, tailored approach right here in the Charleston area.
This guide explores the effectiveness of botox for chronic migraines, common injection sites, treatment frequency, and more, providing hope and clear insights for those seeking lasting relief.
Basics of Botox as a Migraine Treatment
Botox, or onabotulinumtoxinA, represents a targeted approach to managing chronic migraines through neurotoxin intervention. This treatment interrupts pain pathways differently from standard analgesics, offering preventive relief for those with frequent attacks. Understanding its foundational science helps patients in Charleston, SC, evaluate options alongside local providers experienced in neurotoxin therapies.
Mechanism of Action
Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that triggers muscle contractions and pain signal transmission in nerves. In the context of migraines, botox shots for migraines specifically target sensory nerves around the head and neck, reducing the frequency and intensity of headache episodes. Imagine it as a pause button for overactive pain signals; the toxin temporarily paralyzes these pathways, preventing the cascade that leads to full-blown migraines. Clinical evidence shows this inhibition can decrease headache days by up to 50% in responsive patients. For botox injections for migraines, the process involves precise dosing to avoid widespread effects, focusing on peripheral nerve endings. This mechanism distinguishes Botox preventive therapy from reactive treatments, providing long-term relief through injectable migraine relief rather than immediate symptom suppression.
FDA Approval and Eligibility
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Botox for chronic migraines in 2010, following pivotal PREEMPT clinical trials that demonstrated its efficacy. These studies involved over 1,300 participants and revealed that botox for migraines reduced headache days by 8 to 9 on average per month, with 47% of patients experiencing at least a 50% improvement, as detailed in resources like the WebMD guide on the topic. Eligibility typically requires a diagnosis of chronic migraines, defined as 15 or more headache days per month for at least three months, often with moderate to severe pain. Botox for chronic migraines suits adults who have not responded well to at least two prior preventive medications. This approval underscores its role as a validated option in neurology, supported by data showing sustained benefits over multiple cycles. Patients must undergo a thorough assessment to confirm suitability, ensuring the treatment aligns with their migraine pattern.
Basic Safety Profile
Botox treatments carry a favorable safety profile when administered correctly, with most side effects being mild and transient. Common issues arise primarily from the injection process itself, resolving within days to weeks. Key considerations include:
- Pain or tenderness at injection sites
- Temporary neck or muscle weakness
- Mild headaches shortly after treatment
- Eyelid drooping in rare cases
According to WebMD, serious complications occur in less than 1% of cases, emphasizing the importance of professional oversight. Overall, the risk of systemic effects remains low compared to oral medications, as the toxin acts locally. Monitoring for allergic reactions is standard, and dosages are tailored to minimize discomfort. This evidence-based approach supports Botox as a safe choice for eligible patients seeking fewer disruptions from migraines.
Choosing between treatments often depends on lifestyle, tolerance for procedures, and desired outcomes. Comparisons highlight how injectable options like Botox provide focused relief without daily commitments, aiding informed decisions for those in Mount Pleasant exploring alternatives.
| Treatment Type | Administration | Onset of Effect | Duration | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botox Injections | Injections in neck/shoulder/head every 12 weeks | 2-4 weeks | 3 months | Mild pain at injection site |
| Beta-Blockers (e.g., Propranolol) | Daily oral pills | Weeks to months | Ongoing | Fatigue, low blood pressure |
| Antidepressants (e.g., Amitriptyline) | Daily oral pills | 4-6 weeks | Ongoing | Dry mouth, drowsiness, weight gain |
Botox stands out for its targeted action and intermittent schedule, reducing exposure to potential systemic side effects that plague daily orals. Mayo Clinic studies on preventive therapies reinforce this, showing Botox's advantages in patient adherence and localized efficacy for chronic cases. While traditional medications offer broad benefits, their variable results and ongoing use may not suit everyone.
Integration with Local Care
In South Carolina, facilities like the Charleston Ketamine Center in Mount Pleasant provide supervised Botox administration, drawing on expertise in neurotoxins for personalized dosing. This ensures safe, effective care for local patients dealing with persistent migraines. For those in the Charleston area considering Botox preventive therapy, consulting a specialist helps tailor the approach to individual needs. Contact the center at 843-324-6726 for guidance on eligibility and next steps. These fundamentals lay the groundwork; further details on administration sites and protocols follow in subsequent sections.
Exploring Botox Injection Sites and Effectiveness
Botox has emerged as a targeted therapy for chronic migraines, offering relief through precise injections that interrupt pain signals. At Charleston Ketamine Center in Mount Pleasant, South Carolina, led by Dr. Dan Ripley, patients receive this treatment tailored to their needs, ensuring safety and efficacy botox charleston sc. This deep dive examines the specific injection sites and the clinical evidence supporting its use, helping individuals understand how botox injections for migraines can transform daily life.
Key Injection Sites for Migraine Relief
The standard protocol for botox for migraines involves 31 injection sites strategically placed across the head, neck, and shoulders to target peripheral nerves involved in migraine triggers. These sites focus on areas where tension and nerve sensitivity contribute to headache onset, such as the forehead and temples for frontal pain, the back of the head for occipital discomfort, and the neck and shoulders for referred pain from muscle strain. By injecting the neurotoxin into these targeted neurotoxin sites, the treatment blocks the release of acetylcholine, reducing muscle contractions and pain transmission that exacerbate migraines.
Forehead and facial areas receive five injections per side above the eyebrows and in the procerus and corrugator muscles to alleviate tension headaches originating from facial strain. Temples get two injections each to address vascular components often linked to throbbing pain. The back of the head, including the occipitalis and temporalis muscles, requires six sites bilaterally to target nerves radiating from the skull base. Neck muscles like the splenius capitis and trapezius receive the bulk, with 20 sites total, to relieve cervical tension that can trigger cervicogenic migraines. Shoulders incorporate upper trapezius injections to ease shoulder-related referrals.
| Area | Number of Sites | Key Muscles Targeted | Rationale for Migraine Relief |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontalis (Forehead) | 4 (2 per side) | Frontalis | Reduces forehead tension and glabellar frown lines contributing to frontal migraines |
| Corrugator/Procerus | 6 (3 per side) | Corrugator, Procerus | Targets frown muscles to block pain signals from facial nerves |
| Temporalis | 4 (2 per side) | Temporalis | Alleviates temple throbbing by relaxing jaw-adjacent muscles |
| Occipitalis | 6 (3 per side) | Occipitalis | Addresses posterior head pain from occipital nerve irritation |
| Cervic (Neck) | 12 (6 per side) | Splenius Capitis, Semispinalis | Eases neck stiffness that refers pain to the head |
| Trapezius (Shoulders) | 5 (midline and bilateral) | Upper Trapezius | Relieves shoulder tension linked to widespread migraine auras |
Measuring Botox's Impact on Chronic Migraines
Clinical evidence demonstrates that botox for chronic migraines significantly reduces headache frequency and severity, with the PREEMPT trials serving as the foundation for FDA approval. In these Phase III, placebo-controlled studies, participants experienced an average reduction of 8.4 headache days per month compared to 6.6 for placebo, highlighting botox for migraines' preventive benefits.
| Study/Source | Patient Group | Avg. Reduction in Headache Days | Responder Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PREEMPT Trials (FDA Basis) | Chronic migraine patients | 8.4 days | 47-50 |
| Mayo Clinic Follow-up | Real-world users | 7-9 days | 50-60 |
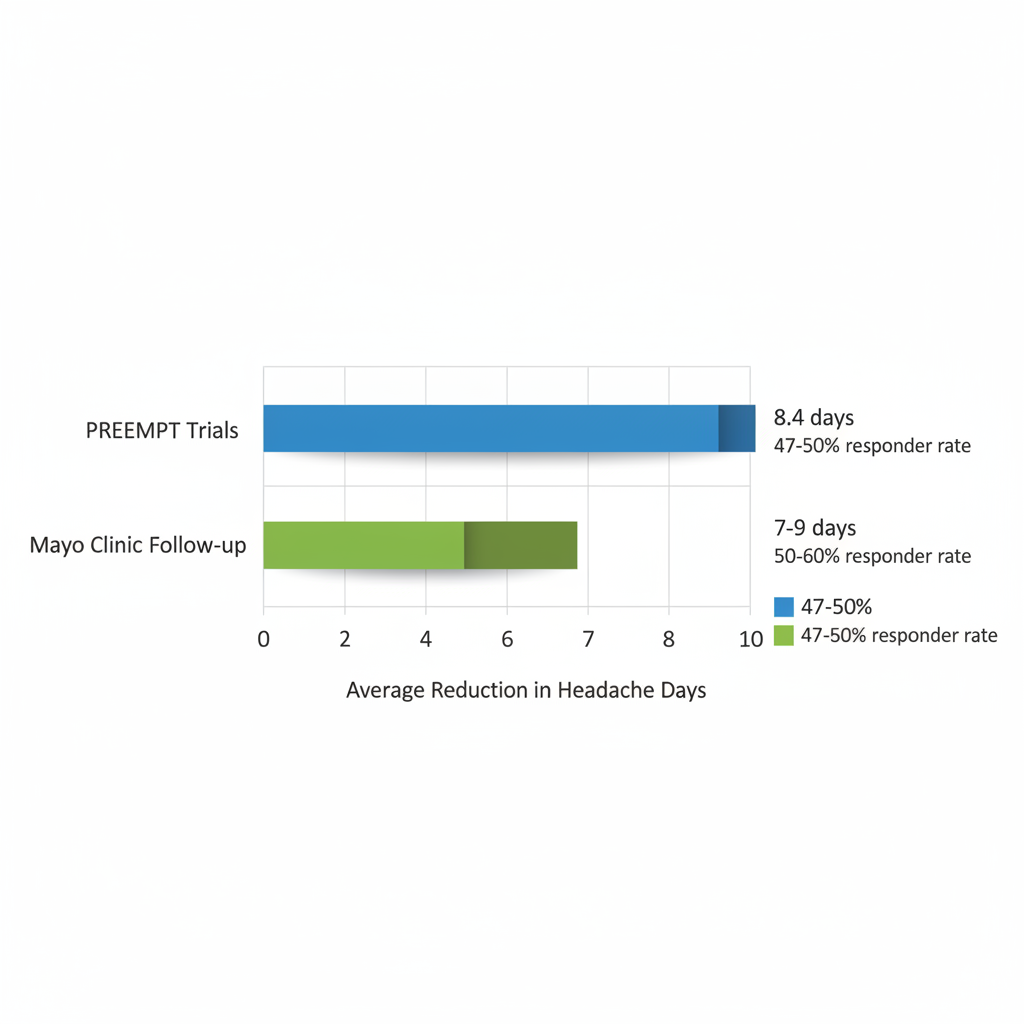
Botox effectiveness comparison in reducing migraine days from key studies
Preparing for and Undergoing Botox Treatment
Preparing for Botox treatment at the Charleston Ketamine Center involves a straightforward process designed for patient comfort and safety. Located in Mount Pleasant, SC, this outpatient clinic specializes in botox mount pleasant sc, offering personalized care for those seeking relief from chronic migraines.
What to Expect During Your Botox Session
Your Botox session at the Charleston Ketamine Center starts with a pre-treatment screening to confirm eligibility and address any concerns. The medical team reviews your migraine history, current medications, and overall health to tailor the approach.
- Consultation and Preparation: Upon arrival, you'll meet with a licensed provider for a quick review. If sensitivity is a concern, a topical numbing agent may be applied to the injection sites.
- Injection Process: The actual injections, targeting 31 specific sites around the head and neck, take about 15-30 minutes, as noted by WebMD guidelines.
- Immediate Aftercare: Right after, you'll receive instructions to avoid rubbing or massaging the treated areas for at least 24 hours to prevent toxin migration.
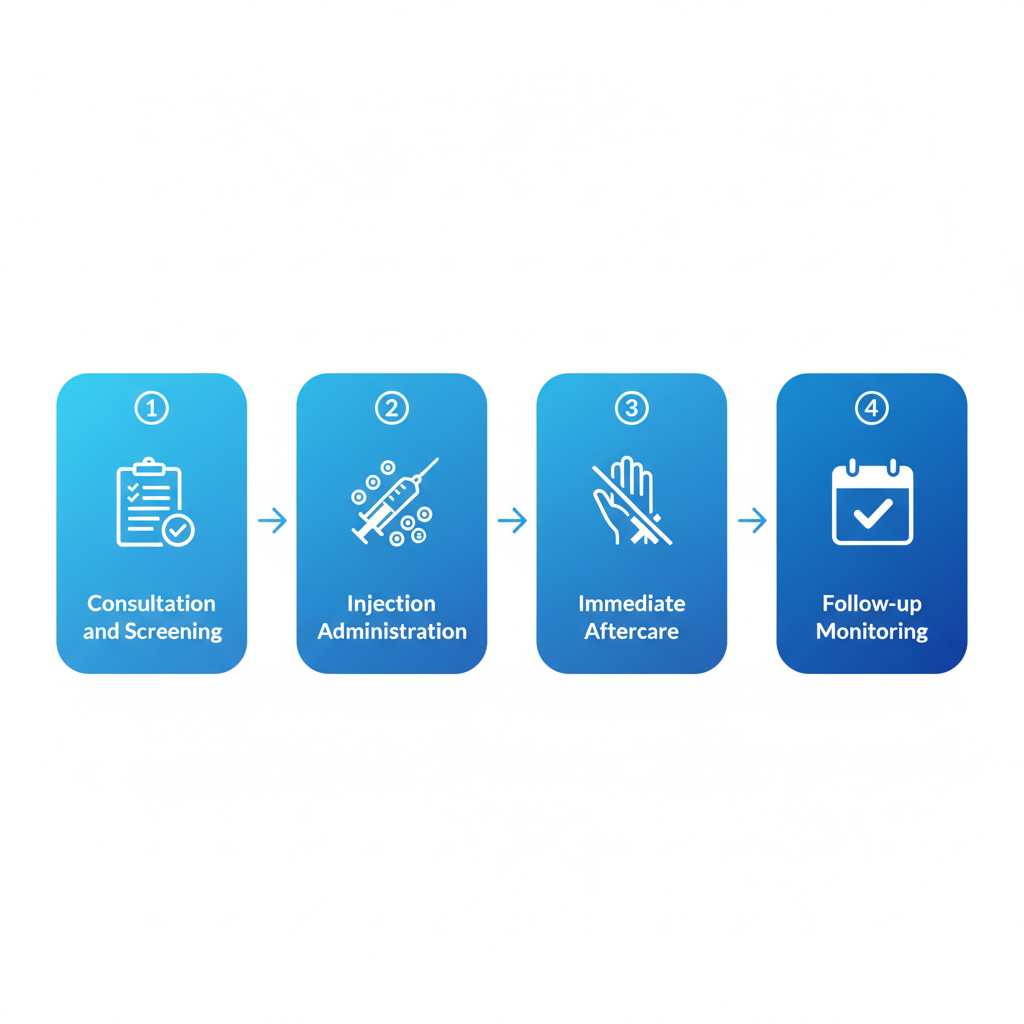
Botox treatment process for migraine relief in four key steps
Administration Schedule and Frequency
The standard administration schedule for botox for migraines follows FDA-approved guidelines, starting with an initial series of treatments every 12 weeks for at least two cycles.
| Aspect | Botox | Trigger Point Injections | Nerve Blocks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Every 12 weeks | Monthly as needed | Every 3-6 months |
| Duration of Effect | 3 months | Weeks | Months |
| Procedure Time | 15-30 min | Targeted relief | Preventive focus |
Advanced Considerations for Botox in Migraine Care
Beyond the basics, advanced Botox protocols for migraine management involve careful attention to financial aspects, potential risks, and innovative combinations that can enhance outcomes.
Cost and Insurance for Botox Treatments
| Factor | With Insurance | Without Insurance | At Charleston Ketamine Center |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Cost | $1,000-$3,000 (copay) | $6,000-$12,000 Fee-for-service | Consultation included Personalized quotes |
| Coverage Criteria | Chronic diagnosis required | Full payment upfront Financing options | Medicare/Medicaid varies Local billing support |
Common Questions About Botox for Migraines
How does Botox work for migraines?
Botox for migraines prevents chronic headaches by blocking nerve signals that trigger pain. Injections target specific head and neck areas to reduce migraine frequency over time.
What are the side effects of Botox for migraines?
Common side effects include temporary muscle weakness or neck pain, which typically resolve within weeks, as noted in medical sources. Serious reactions are rare.
Next Steps for Migraine Relief with Botox
Botox injections for migraines offer a proven mechanism by blocking nerve signals that trigger pain, reducing attack frequency by up to 50% for many patients.